
Lasers can be absorbed inside an optical substrate through several different methods. Electrons in discrete energy levels of the atoms that make up the optical medium absorb radioactive photons and are pushed to semi-stable, higher energy levels. These atoms then fluoresce and emit radiation (photons) through spontaneous emission when electrons fall back to a lower energy level. Unintentional fluorescence causes loss of energy and interference with signal detection, which can be detrimental in sensitive applications. Fluorescence is often nearly isotropic and radiates in all directions, which makes things worse. Fluorescence is typically caused by impurities in the substrate such as rare earth ions.
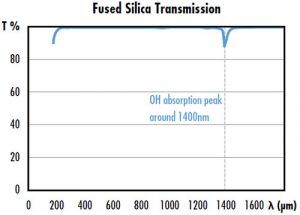
Optical media may also absorb radiation in the form of thermal energy or heat. Hot spots are local excesses of heat caused bymaterial inhomogeneity or subsurface damage and cause optics to degrade much more quickly. Exposure to high-energy radiation, such as UV or X-rays, solarize a material, changing its color and increasing absorption by forming color centers that absorb specific wavebands. Therefore, it is important to understand how, and in what ways different types of radiation, including laser radiation, are absorbed by different glass types in order to mitigate damage.